What Causes Sudden Abdominal Pain? Understanding the Culprits Behind this common issue:

Sudden abdominal pain can feel like — a sharp twinge, a dull ache, or a deep cramp that leaves you keep clutching your stomach. It’s one of the most frequent reasons of people seek emergency medical care. while some causes are harmless and pass by on their own, others may be urgent, even few of them can be life-threatening. So what exactly causes sudden abdominal pain? Lets have a look upon.
Causes of Sudden Abdominal Pain:
1. Digestive System Disruptions
One of the most common sources of sudden abdominal pain comes from the digestive tract. The gastrointestinal (GI) system is a long and winding network, and problems at any point can trigger discomfort then eventually Pain begins.
– Gas or indigestion: Often underestimated, trapped gas or acid reflux can cause sharp or burning pain, especially after eating. It can feels as a more serious issues, but usually it resolves within hours.
– Gastroenteritis: Commonly known as the stomach flu (although it is not associated with influenza), this is also known as infectious diarrhea. Symptoms come on quickly—nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and cramping. Typically caused by viral or bacterial infections when eating improperly prepared food or unhygienic food, drinking contaminated water.
– Intestinal colic: it is most frequently associated with periumbilical pain and abdominal distension: the more distal in the intestine the pathology, the greater the degree of distension.
– Constipation: When stool builds up in the colon, it can cause bloating and cramp-like pain.
2. Inflammatory Conditions
Sometimes the abdominal pain is a signal of an inflammation in the abdominal organs, which could point to a specific condition:
– Appendicitis: Often starting with pain near the belly button (Umblicus) and shifting to the lower right abdomen that why it’s characterized by Shifting Pain (Shifting of pain). Appendicitis is a medical emergency. Delaying in treatment often risks a rupture.
– Diverticulitis: Inflammation or infection in small pouches of the large intestine (colon) wall can cause left abdominal pain, often accompanied by loss of appetite, fever & Chills and nausea/vomiting.
– Pancreatitis: Inflammation of the pancreas leads to upper abdominal pain that may radiate to the back, as pancrease is located behind the stomach. Pain felt in the upper left or upper middle of abdomen. Characteristic feature of the Pancreatitis is worsening of pain after meals (specifically high Fat meal). Pain may even worse when lying on back. Acute pancreatitis often has an abrupt onset of severe epigastric pain radiating to the back, which may be similar to pain emanating from stomach ulcer perforation or a leaking Abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA).
3. Other Abdominal Organs urgent Surgical Issues
This are the causes Abdominal Pain which needs an urgent medical intervention to prevent serious complications.
– Gallstones:
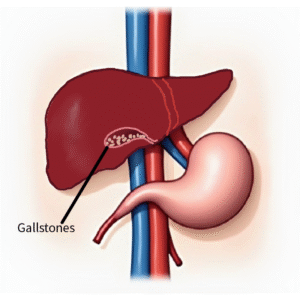
Sudden abdominal pain in the upper right abdomen, often after eating fatty foods, as stones blocking the gallbladder or bile duct causes obstruction to flow of bile leads to pain. When the gall bladder contracts against a stone, pain is relatively insidious in begining and reaches its peak in about half an hour and then eases off. But basal pain persists between the bouts of colic.
– Kidney stones:
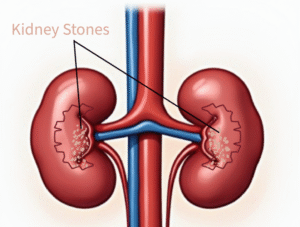
Its causes excruciating pain that radiates from the back of lumbar region (flanks) to the groin, kidney stones can strike suddenly and without warning. It can be associated with hernia.
– Intestinal obstruction:
Whether due to scar tissue, hernias, or tumors, blockages in the intestines can cause severe, cramping pain and requires an urgent care. Vomiting is an early feature of proximal small Intestinal obstruction, whereas absolute constipation is an early feature of colonic obstruction.
![]() Colicky Abdominal Pain
Colicky Abdominal Pain
● Pain of ‘small Intestinal colic’ comes in waves and disappears completely in minutes when the peristaltic wave ceases.
● Pain of biliary colic is insidious in onset, reaches the peak in half an hour or so and does not ease off completely between spasms.
● Pain of ureteric colic is intense lasting one to two minutes of the ureter emptying.
4. Reproductive System issues that Causes Sudden Abdominal Pain
The reproductive systems pathology causes lower abdominal pain mostly in females, originate from the gynecological problems.
– Ovarian cyst rupture: A sharp sudden pain in one side of the lower abdomen can be due to a ruptured ovarian cyst.
– Ectopic pregnancy: A pregnancy outside the uterus (often in a fallopian tube) can cause pain and internal bleeding, if it ruptures then it’s a critical emergency.
– Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID): Infection of the reproductive organs can cause lower abdominal pain, fever, and abnormal discharge.
5. Vascular Emergencies
Rare but deadly, some causes of Sudden abdominal pain that originates from:
– Abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA): A tear or rupture in the main artery in the abdomen can cause sudden, severe pain and must be treated immediately to save patients life.
– Mesenteric ischemia: This occurs when blood flow to the intestines is blocked, causing pain out of proportion to exam findings.
*Visceral pain arises from ischemia, muscle spasm or stretching of the visceral peritoneum.
*Visceral pain from the foregut is generally felt in the epigastrium, in the periumbilical area from the mid-gut and in the suprapubic area from the hind-gut.
6. Stress and the Mind-Gut Connection
Interestingly, not all abdominal pain originates from the physical cause. The gut is highly responsive to emotional stress due to the brain-gut connection. Sometimes, When no organic cause can be found for abdominal pain, this situation often labelled as ‘functional abdominal pain’. Improved understanding of pain pathways and the relationship with the gastrointestinal microbiome is likely to provide a more precise diagnosis, particularly in a common ‘functional’ disorders such as non-ulcer dyspepsia and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS).
– Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) : Though not dangerous, IBS can cause sudden cramping, bloating, and bowel changes.
– Anxiety-related pain: Stress and panic attacks can cause abdominal discomfort that feels very real, though no physical cause can be found upon diagnosis.
What treatment is available for Sudden Abdominal Pain?
1. Treatment for the Digestive Tract Issues like:
Gas / Indigestion / Heartburn:
Antacids (Tums-calcium carbonate, Pepcid-famotidine 40mg, etc.), avoiding trigger foods and carbonated drinks, do sipping water, light activity like walking. In case of diarrhea along with heartburn and indigestion Pepto Bismol can be taken.
Constipation
Treatment: Hydration, fiber supplements, stool softeners (Colace), mild laxatives, and exercise.
Gastroenteritis
Treatment: Rest, fluids with electrolytes, anti-nausea meds (like ondansetron), and a light diet.
Note: Antibiotics may be needed if bacterial infections are suspected.
2. Treatment for Inflammatory Conditions like:
Appendicitis
Treatment: Emergency surgery (appendectomy). Sometimes antibiotics are used first to decrease bacterial load.
Diverticulitis
Treatment: Antibiotics, clear liquid diet during peak, and pain relievers. Surgery in severe or recurring cases.
Pancreatitis
Treatment: Hospitalization is must, start with IV fluids, pain control, no food should be given until inflammation reduces. Sometimes surgery or interventions needed to remove gallstones obstructing the bile duct.
Surgical Emergencies for Other Abdominal Organs
Gallstones
Treatment: Pain management, diet changes, and often gallbladder removal (cholecystectomy) surgery is adviced.
Kidney Stones
Treatment: Pain relief, hydration to pass the stone, or procedures like lithotripsy or surgical removal if stone is larger that 5mm size.
Intestinal Obstruction
Treatment: Hospital care with IV fluids, bowel rest (nothing by mouth), and sometimes surgery to remove the blockage.
4. Reproductive Causes in Women
Ovarian Cyst Rupture
Treatment: Pain control, monitoring, rarely surgery unless bleeding is severe.
Ectopic Pregnancy
Treatment: Emergency medical or surgical treatment to prevent rupture and bleeding.
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID)
Treatment: Antibiotics, sometimes hospitalization if severe.
5. Vascular Emergencies
Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm (AAA)
Treatment: Emergency surgery to stop bleeding by repairing the affected artery.
Mesenteric Ischemia
Treatment: Emergency surgery or angioplasty to restore blood flow, along with antibiotics.
6. Stress or Functional Conditions
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
Treatment: Dietary changes, stress management, antispasmodics, fiber supplements, and probiotics.
Anxiety-related pain
Treatment: Stress reduction (therapy, mindfulness, exercise, meditation), antianxiety medications if needed.
 When to Seek Medical Attention ?
When to Seek Medical Attention ?
While many causes of Sudden abdominal pain are benign, it’s important to recognize red flags:
– Pain that is severe or worsening
– Pain with free liquid flow feel in the abdomen.
– Pain accompanied by fever, vomiting, or bloody stools
– Abdominal swelling or rigidity
– Pain following trauma
– Inability to pass gas or stool
![]() Doctor (Gastroenterologist or General Surgeon) will do the Physical examination in systematic way using the following sequence: inspection, palpation, percussion and auscultation. And Prescribe the required treatment.
Doctor (Gastroenterologist or General Surgeon) will do the Physical examination in systematic way using the following sequence: inspection, palpation, percussion and auscultation. And Prescribe the required treatment.
Reference: Bailey & Love’s Short Practice Of Surgery, 27Th Edition: International Student’s Edition